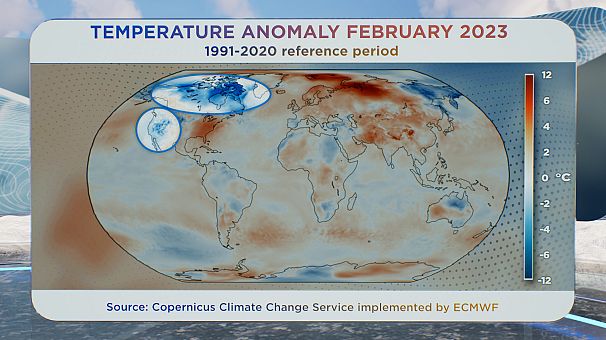
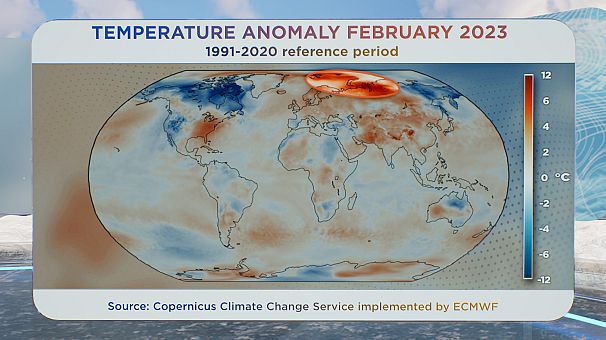
Temperatures in elements of the Arctic had been six levels or extra above common in February.
It is troublesome to forecast with certainty the pace at which local weather change will rework our planet's northern polar area, nonetheless researchers are observing that the ice is thinning quickly, and fashions predict that ice-free Arctic summers are on the horizon.
On this particular episode of Local weather Now, we travelled to Tromsø in northern Norway to listen to extra from sea ice specialists on the Norwegian Polar Institute.
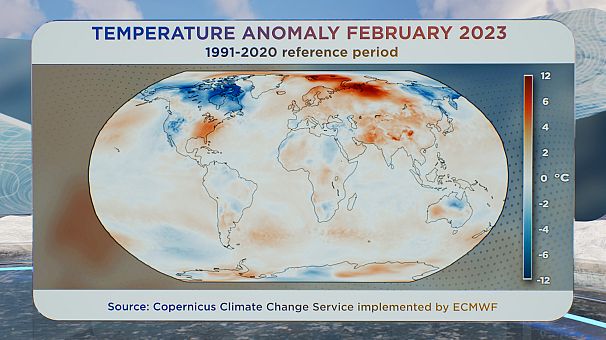
The fifth-warmest February on report
Knowledge from the Copernicus Local weather Change Service reveals that globally, February 2023 was the fifth-warmest on report, with temperatures 0.3° Celsius above the 1991-2020 common.
If we have a look at the temperature anomaly map worldwide we are able to see a number of standout options.
Firstly, in northern Canada and elements of the western US, temperatures had been a number of levels under common:
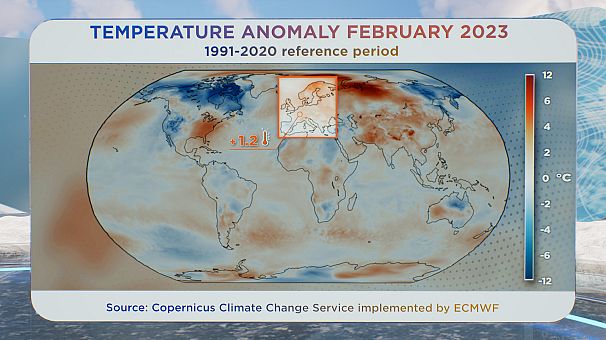
In Europe, it was typically hotter - temperatures for February had been 1.2° Celsius above common for the month:
After which, in darkish pink, above Norway and Russia, temperatures had been 6° or extra above common in February.
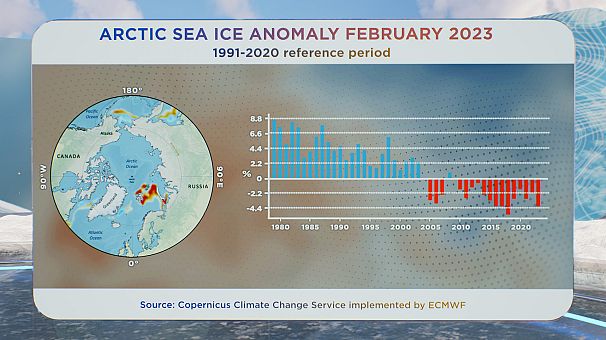
And people hotter temperatures within the Arctic final month come at a time of 12 months when sea ice must be plentiful on the finish of winter.
Sea ice extent was at its second-lowest degree on report for February, and sea ice focus was decrease than common within the areas shaded in pink on the map round western Siberia, and Svalbard.
Arctic is warming a lot sooner than world common
On the Norwegian Polar Institute in Tromsø, contained in the Arctic Circle, researchers are finding out the influence of local weather change on the area.
The Arctic is warming three to 4 instances sooner than the worldwide common, and sea ice scientist Mats Granskog tells Euronews that he has witnessed the modifications together with his personal eyes
"Once I first ventured on the market possibly 20 years in the past, it was quite a lot of pack ice - thick, heavy ice," he says. "These days, some years we have now a tough time to really discover a piece of ice, an ice floe to work on. So it is modified fairly dramatically over the previous a long time."
Ice is turning into thinner
Yearly the scientists sail to the northeast of Greenland to gather samples on the way in which to the North Pole - after which deliver them again to Tromsø for examine. They do not make all of it the way in which to 90 levels north yearly, it will depend on the ice, however in 2022 it was comparatively plain crusing.
The Arctic sea ice cores are saved at -24°C in had giant freezer room, and every ice core represents a snapshot of the Arctic on the time it was sampled.
"This one was taken late July final summer season after we reached the North Pole," Mats reveals us. "So we roughly had a metre and a half of sea ice on the North Pole final summer season. Sometimes, we might have within the order of three metres of ice 20 years in the past."
Within the frozen lab subsequent door, Dimitry Divine research how the ice was fashioned. The key modifications he sees are within the age and thickness of the ice.
"The ice is getting thinner and thinner," he explains. "It will not be capable to survive the summer season soften."
Older sort of ice are disappearing
Local weather change impacts the overall age of the ice as nicely. Researchers distinguish between first-year ice and multi-year ice. The Arctic would usually have a mixture of each, however the central Arctic and areas north of Canada historically have extra multi-year ice. However because it warms, the older ice is disappearing.
"The ice within the Arctic is usually now dominated by the first-year ice kinds," says Dimitry. "The older kinds of ice, which might have prevailed for 20, 30 years in the past within the central Arctic, they're roughly gone."
"We see, particularly within the western Arctic, the elevated quantities of snow, precipitation on the ice all through the final decade," he provides. "And that's associated with the actual fact of a hotter and extra humid Arctic on the whole."
Suggestions loops
The Arctic warming is partly resulting from what are generally known as suggestions loops - one instance is that open seawater is darker than ice, so it warms up sooner, and accelerates the soften. Nonetheless, there's nonetheless lots we do not grasp about this polar area.
"Sea ice relies on the environment and the ocean under. And it is a moderately complicated system to grasp. And I assume the large questions are what is going to the Arctic appear to be sooner or later? And that is a troublesome one, I feel, as a result of we do not but absolutely perceive the way it's functioning in the present day," says Mats.
"The forecasts or our local weather fashions tells us that there will definitely be a time after we can contemplate the Arctic as ice-free in the summertime. However when precisely that can occur, there is a good bit of uncertainty, and we do not know all of the suggestions within the system. And I sense that we do not know if it is going to be simply gradual or we can have some sort of abrupt modifications which switches the system to a totally new state. And that is an lively discipline of analysis: to grasp all this suggestions mechanism within the system that may really speed up the warming."

Post a Comment